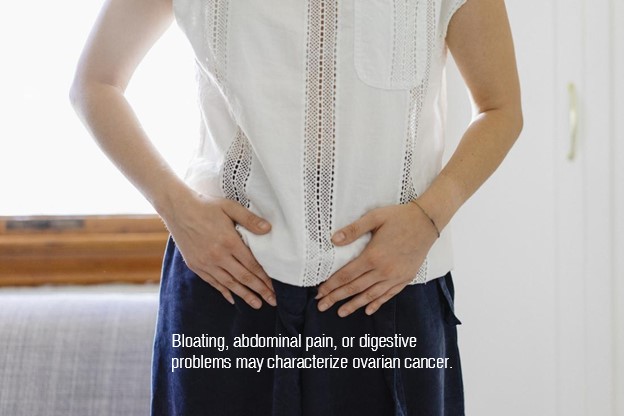
It is regularly hard to analyze ovarian malignant growth in its beginning phases in light of the fact that the side effects are like those of different conditions. Any individual who encounters unexplained stomach indications that keep going for over about fourteen days should see a specialist.
Ovarian malignancy can likewise be trying to distinguish early on the grounds that the ovaries are little and found somewhere down in the midsection, making any developments that may be on them difficult for a specialist to feel.
As indicated by the National Ovarian Cancer Coalition (NOCC), just around 19 percent of ovarian malignancy is analyzed in the beginning phases.
What are the early indications of ovarian malignancy?
Ovarian malignant growth doesn’t bring about any perceptible manifestations in the beginning phases.
The indications most connected with ovarian malignancy will in general create in the later phases of the condition, as developments put focus on the bladder, uterus, and rectum.
Be that as it may, these manifestations of ovarian malignant growth can create at any phase of the condition and include:
- bloating
- pelvic or stomach torment or squeezing
- feeling full rapidly in the wake of beginning to eat or absence of hunger
- indigestion or agitated stomach
- nausea
- the need to pee more often or desperately than ordinary
- a pressure in the lower back or pelvis
- unexplained weariness
- back torment
- constipation
- increase stomach bigness or stomach expanding
- painful sex
- menstrual changes
- weight misfortune
These side effects can be because of an assortment of different conditions, which will frequently react to fundamental treatment or disappear all alone.
Be that as it may, if these indications grow out of nowhere and persevere, or proceed with pretty much day by day paying little mind to fundamental therapy, consider a to be for a determination as they may be manifestations of ovarian disease.
When to see a specialist
Since it is hard to analyze ovarian malignancy at a beginning phase, most wellbeing specialists recommend that the most ideal approach to help lessen the odds of growing further developed phases of ovarian malignancy is by taking a positive, proactive way to deal with the malady.
To guarantee the absolute best result, an individual should converse with their family specialist or the gynecologist about any likely manifestations as quickly as time permits.
Signs can incorporate any unexplained side effects of ovarian malignant growth, or any new stomach or pelvic manifestations, that:
- are inconsequential to another analyzed condition
- do not react to fundamental treatment, for instance, back agony that doesn’t disappear with rest and icing, or heartburn that doesn’t improve with diet changes and exercise
- last for over about fourteen days
- occur for over 12 days every month
Danger factors
Danger factors that may make a few people bound to create ovarian malignancy than others include:
- a family background of bosom, ovarian, or uterine malignancy
- having the BRCA1 and BRAC2 quality
- having Lynch disorder
- never being pregnant
- obesity
- some richness and hormone meds
- endometriosis
- age, most cases create after menopause
Individuals with a family background of conceptive or gastrointestinal malignant growths should converse with their PCP or gynecologist about going through hereditary advising to test whether they convey explicit quality transformations that may expand their danger of ovarian disease.
Variables that may bring down generally danger of creating ovarian malignancy include:
- being pregnant
- choosing to breastfeed
- using oral conception prevention prescriptions for at any rate 5 years
- having regenerative framework medical procedures, for example, a hysterectomy, ovarian evacuation, or tubal ligation
Conclusion
Encountering a portion of the side effects related with ovarian malignant growth doesn’t imply that an individual has the ailment. Ovarian malignancy can’t act naturally analyzed at home. Analysis requires a scope of tests and ordinarily the association of an expert.
To analyze ovarian malignant growth, a specialist will begin by posing inquiries about manifestations including:
- when they started
- how they have reacted to fundamental treatment
- how long an individual has had them
- how regularly they happen
The specialist will go over an individual’s clinical history and pose inquiries about their family background of malignancy, particularly any history of ovarian and bosom disease. The specialist will play out a pelvic test to check whether the ovaries are kindled, extended, or if there is liquid in the midsection.
A specialist will arrange extra testing if:
- they note any irregularities during the pelvic test
- symptoms demonstrate an individual may have ovarian disease
- an individual’s clinical or family ancestry makes them bound to create ovarian disease
Previously or after these tests, a specialist will allude the person to a gynecologic oncologist — a specialist that spends significant time in treating malignant growths of the regenerative framework. The oncologist will enable an individual to choose the most ideal approach with treating and dealing with the condition.
The tests that specialists utilize most regularly to distinguish ovarian disease at first include:
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS)
In this test, a specialist embeds an ultrasound test into the vagina. The test transmits ultrasound waves that reverberation back, creating a picture of the uterus, fallopian cylinders, and ovaries.
This test can help recognize likely developments and decide if they are strong developments or sores, which are non-harmful, liquid filled sacs.
On the off chance that the specialist distinguishes a strong development, they will presumably demand a biopsy to decide if the development is destructive or kind (non-dangerous).
CA-125 blood test
The CA-125 blood test quantifies the measure of the protein CA-125 that is in the blood. Numerous individuals with ovarian malignant growth have elevated levels of CA-125 in their blood.
Nonetheless, those with other, less serious conditions, for example, pelvic incendiary ailment (PID) and endometriosis, frequently have significant levels of this protein in their blood, as well.
Only one out of every odd lady with ovarian malignancy has raised degrees of CA-125 in their blood. As indicated by the Ovarian Cancer Research Fund Alliance (OCRFA), around 80 percent of those with cutting edge ovarian malignancy have raised degrees of CA-125, while 50 percent experience elevated levels in the beginning phases of the condition.
Computed tomography (CT) examines
CT examines include passing extraordinary X-beams through the mid-region. A PC measures the outcomes to make cross-sectional pictures that permit specialists to see areas of the stomach depression and pelvis.
Biopsy
A biopsy involves inserting a very fine needle into the body and withdrawing a small section of the growth or mass, which is sent to a laboratory to check for signs of cancer. The results of a biopsy are an essential element in making a final diagnosis of ovarian cancer.
Screening methods and prevention
Despite research efforts, there are currently no screening methods available to detect ovarian cancer in people who do not have any symptoms or who are not at a higher risk than usual for developing the condition.
How probably is it that manifestations demonstrate malignant growth?
Ovarian disease is a moderately uncommon type of malignant growth, speaking to an expected 1.3 percent of all disease cases recently analyzed in 2018 in the United States. This implies the manifestations related with ovarian malignant growth are considerably more liable to be brought about by other, far less serious conditions than ovarian disease.
Standpoint
Around 94 percent of individuals who get an analysis and therapy of ovarian disease in the beginning phases endure over 5 years after determination.
Somewhere in the range of 2008 and 2014, about 47.4 percent of individuals in the U.S. lived for in any event 5 years after an ovarian malignant growth analysis.
The demise rate patterns among those with ovarian malignant growth have been reliably dropping. The National Cancer Institute gauge that ovarian malignancy will represent 2.3 percent of all disease passing in 2018.
Takeaway
Since manifestations of ovarian malignancy have similitudes to numerous other, typically less perilous conditions, numerous ladies neglect the signs. Since the ovaries are found somewhere down in the body, it is practically inconceivable, in any event, for specialists, to feel little developments on the organs.
Any individual who has unexplainable pelvic or stomach manifestations that are extreme, keep going for over about fourteen days, or don’t disappear with essential consideration should converse with their PCPs as quickly as time permits.
It is additionally a smart thought for the individuals who have a solid family background of bosom, ovarian, uterine, or colon malignant growth to converse with their PCPs about going through hereditary directing.